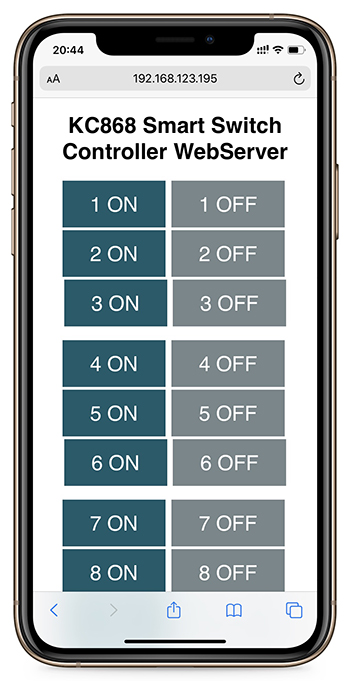
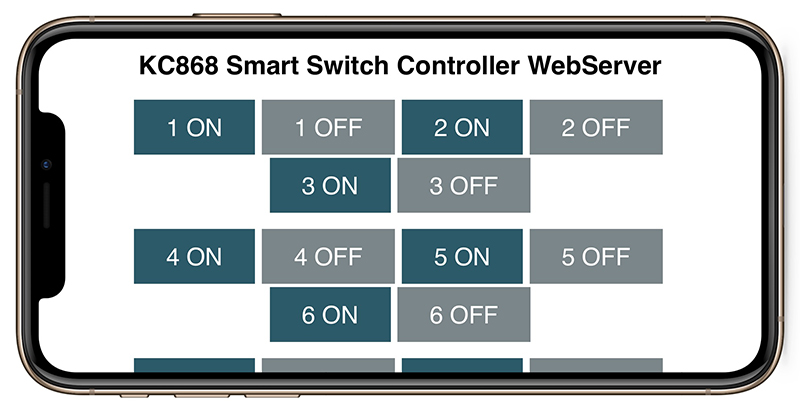
This tutorial is a step-by-step guide that shows how to build a standalone ESP8266 Web Server that controls KC868-Hx Controller’s relays. This ESP8266 NodeMCU Web Server is mobile responsive and it can be accessed with any device with a browser in your local network, such as mobile phone and PC or MAC’s browser , also it not need internet,

Build Web Server Using ARDUINO IDE
Now we show you how to build a web server to control relay outputs using Arduino IDE. You can use this method to create a different web server to fulfill your needs.
Prepare the Arduino IDE
1. Download and install the Arduino IDE on your operating system , such as Windows OS or MAC OS according to you.
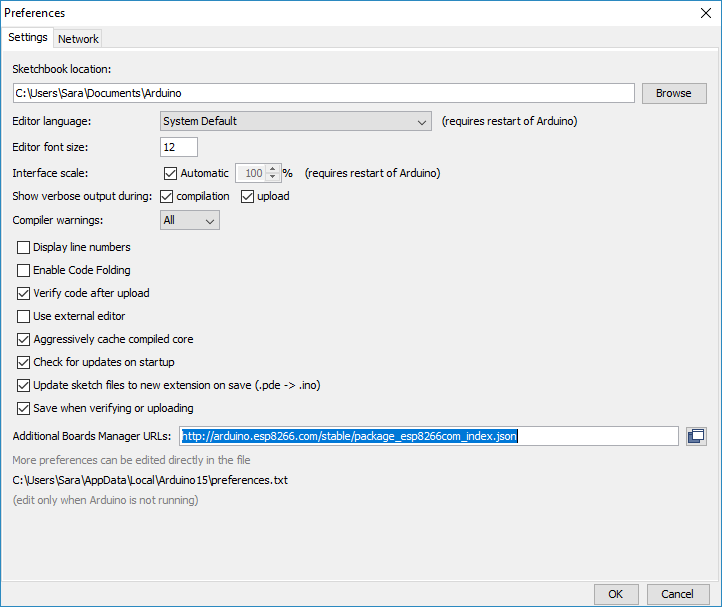
2. Then, you need to install the ESP8266 add-on for the Arduino IDE. For that, go to Menu File > Preferences.
3. Enter http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json into the “Additional Board Manager URLs” field as shown in the figure below. Then, click the “OK” button.
4. Go to Tools > Board > Boards Manager…

5. Scroll down, select the ESP8266 board menu and install “esp8266 by ESP8266 Community”, as shown in the figure below.
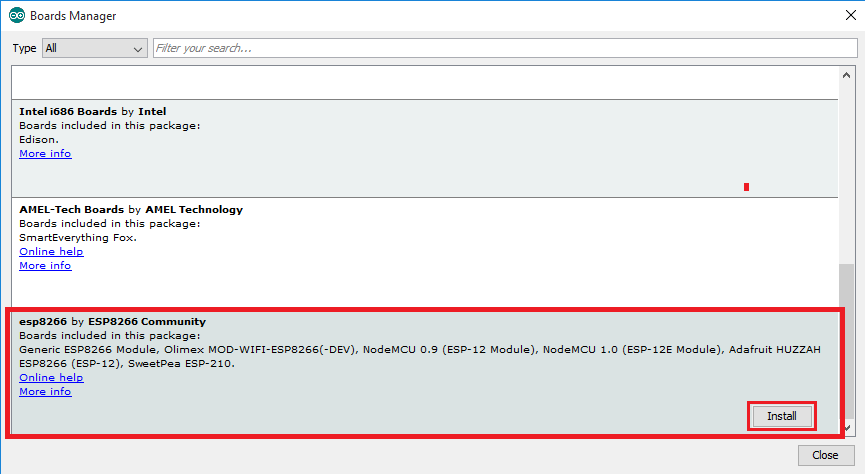
6. Go to Tools > Board and choose your ESP8266 board. Then, re-open your Arduino IDE.
Code
Following code to your Arduino IDE. You need to make some changes to make it work for you,this demo code show 2 relays control.
/**********************************************************
* Create Your own WebServer for KC868-Hx Smart Controller*
* https://www.kincony.com **
***********************************************************/
// Load Wi-Fi library
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = “KinCony”; //your router’s ssid
const char* password = “KinCony”; //your router’s password
// Set web server port number to 80
WiFiServer server(80);
// Variable to store the HTTP request
String header;
// Current time
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
// Previous time
unsigned long previousTime = 0;
// Define timeout time in milliseconds (example: 2000ms = 2s)
const long timeoutTime = 2000;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); //Bule LED of WiFi Module
// Connect to Wi-Fi network with SSID and password
// Serial.print(“Connecting to “);
// Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
// Serial.print(“.”);
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); //WiFi Connect fail,Blue LED OFF
}
// Print local IP address and start web server
// Serial.println(“”);
// Serial.println(“WiFi connected.”);
// Serial.println(“IP address: “);
// Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
server.begin();
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); //WiFi Connect OK,Blue LED ON
}
void loop(){
WiFiClient client = server.available(); // Listen for incoming clients
if (client) { // If a new client connects,
// Serial.println(“New Client.”); // print a message out in the serial port
String currentLine = “”; // make a String to hold incoming data from the client
currentTime = millis();
previousTime = currentTime;
while (client.connected() && currentTime – previousTime <= timeoutTime) { // loop while the client’s connected
currentTime = millis();
if (client.available()) { // if there’s bytes to read from the client,
char c = client.read(); // read a byte, then
// Serial.write(c); // print it out the serial monitor
header += c;
if (c == ‘\n’) { // if the byte is a newline character
// if the current line is blank, you got two newline characters in a row.
// that’s the end of the client HTTP request, so send a response:
if (currentLine.length() == 0) {
// HTTP headers always start with a response code (e.g. HTTP/1.1 200 OK)
// and a content-type so the client knows what’s coming, then a blank line:
client.println(“HTTP/1.1 200 OK”);
client.println(“Content-type:text/html”);
client.println(“Connection: close”);
client.println();
// turns 32 relays on and off
if (header.indexOf(“GET /1/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,1,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /1/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,1,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /2/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,2,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /2/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,2,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /3/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,3,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /3/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,3,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /4/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,4,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /4/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,4,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /5/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,5,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /5/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,5,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /6/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,6,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /6/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,6,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /7/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,7,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /7/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,7,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /8/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,8,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /8/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,8,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /9/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,9,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /9/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,9,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /10/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,10,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /10/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,10,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /11/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,11,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /11/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,11,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /12/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,12,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /12/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,12,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /13/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,13,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /13/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,13,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /14/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,14,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /14/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,14,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /15/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,15,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /15/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,15,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /16/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,16,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /16/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,16,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /17/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,17,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /17/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,17,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /18/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,18,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /18/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,18,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /19/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,19,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /19/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,19,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /20/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,20,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /20/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,20,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /21/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,21,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /21/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,21,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /22/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,22,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /22/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,22,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /23/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,23,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /23/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,23,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /24/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,24,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /24/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,24,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /25/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,25,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /25/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,25,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /26/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,26,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /26/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,26,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /27/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,27,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /27/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,27,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /28/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,28,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /28/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,28,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /29/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,29,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /29/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,29,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /30/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,30,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /30/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,30,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /31/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,31,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /31/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,31,0”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /32/on”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,32,1”);
else if (header.indexOf(“GET /32/off”) >= 0) Serial.print(“RELAY-SET-255,32,0”);
// Display the HTML web page
client.println(“<!DOCTYPE html><html>”);
client.println(“<head><meta name=\”viewport\” content=\”width=device-width, initial-scale=1\”>”);
client.println(“<link rel=\”icon\” href=\”data:,\”>”);
// CSS to style the on/off buttons
// Feel free to change the background-color and font-size attributes to fit your preferences
client.println(“<style>html { font-family: Helvetica; display: inline-block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;}”);
client.println(“.button { background-color: #195B6A; border: none; color: white; padding: 16px 40px;”);
client.println(“text-decoration: none; font-size: 30px; margin: 2px; cursor: pointer;}”);
client.println(“.button2 {background-color: #77878A;}</style></head>”);
// Web Page Heading
client.println(“<body><h1>KC868 Smart Switch Controller WebServer</h1>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/1/on\”><button class=\”button\”>1 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/1/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>1 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/2/on\”><button class=\”button\”>2 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/2/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>2 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/3/on\”><button class=\”button\”>3 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/3/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>3 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/4/on\”><button class=\”button\”>4 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/4/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>4 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/5/on\”><button class=\”button\”>5 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/5/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>5 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/6/on\”><button class=\”button\”>6 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/6/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>6 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/7/on\”><button class=\”button\”>7 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/7/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>7 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/8/on\”><button class=\”button\”>8 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/8/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>8 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/9/on\”><button class=\”button\”>9 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/9/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>9 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/10/on\”><button class=\”button\”>10 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/10/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>10 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/11/on\”><button class=\”button\”>11 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/11/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>11 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/12/on\”><button class=\”button\”>12 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/12/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>12 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/13/on\”><button class=\”button\”>13 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/13/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>13 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/14/on\”><button class=\”button\”>14 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/14/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>14 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/15/on\”><button class=\”button\”>15 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/15/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>15 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/16/on\”><button class=\”button\”>16 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/16/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>16 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/17/on\”><button class=\”button\”>17 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/17/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>17 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/18/on\”><button class=\”button\”>18 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/18/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>18 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/19/on\”><button class=\”button\”>19 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/19/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>19 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/20/on\”><button class=\”button\”>20 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/20/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>20 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/21/on\”><button class=\”button\”>21 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/21/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>21 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/22/on\”><button class=\”button\”>22 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/22/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>22 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/23/on\”><button class=\”button\”>23 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/23/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>23 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/24/on\”><button class=\”button\”>24 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/24/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>24 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/25/on\”><button class=\”button\”>25 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/25/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>25 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/26/on\”><button class=\”button\”>26 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/26/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>26 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/27/on\”><button class=\”button\”>27 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/27/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>27 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/28/on\”><button class=\”button\”>28 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/28/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>28 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/29/on\”><button class=\”button\”>29 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/29/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>29 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/30/on\”><button class=\”button\”>30 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/30/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>30 OFF</button></a><p>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/31/on\”><button class=\”button\”>31 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/31/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>31 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/32/on\”><button class=\”button\”>32 ON</button></a>”);
client.println(“<a href=\”/32/off\”><button class=\”button button2\”>32 OFF</button></a>”);
client.println(“</body></html>”);
// The HTTP response ends with another blank line
client.println();
// Break out of the while loop
break;
} else { // if you got a newline, then clear currentLine
currentLine = “”;
}
} else if (c != ‘\r’) { // if you got anything else but a carriage return character,
currentLine += c; // add it to the end of the currentLine
}
}
}
// Clear the header variable
header = “”;
// Close the connection
client.stop();
// Serial.println(“Client disconnected.”);
// Serial.println(“”);
}
}
You need to modify the following two variables with your network credentials, so that your ESP8266 can establish a connection with your router by WiFi.
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "";
const char* password = "";Download the RAW Arduino Code
Uploading the Code
Uploading program to the ESP-12E
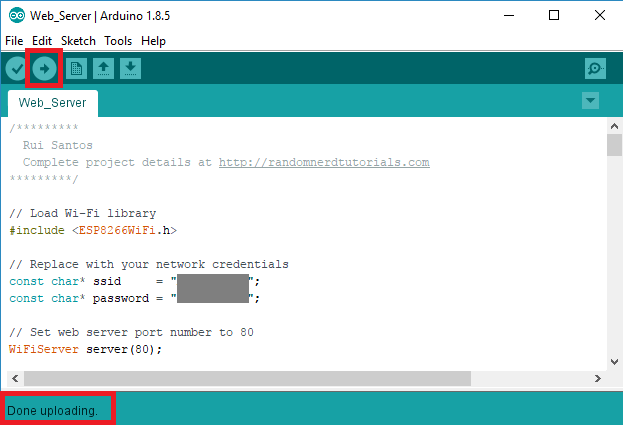
Then, click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE and wait a few seconds until you see the message “Done uploading.” in the bottom left corner.
Testing the Web Server
Now, you can upload the code, and it will work straight away. Don’t forget to check if you have the right board and COM port selected, otherwise you’ll get an error when trying to upload. Open the Serial Monitor at a baud rate of 115200.
Finding the ESP8266 IP Address
Press the ESP8266 RESET button, and it will output the ESP IP address on the Serial Monitor
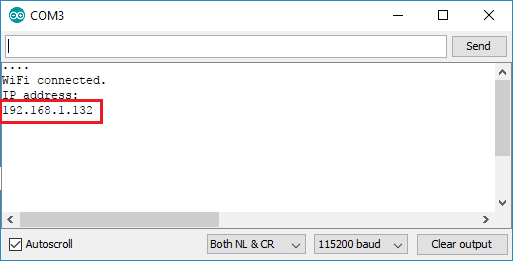
Copy that IP address, because you need it to access the web server.
When Web server connect to your router Successfully, module bule LED will be ON, and you can see your Web Server IP address on your router’s client list.
Accessing the Web Server
Open your browser, type the ESP8266 IP address, and you’ll see the following page. This page is sent by the ESP8266 when you make a request on the ESP IP address.

We can also use URL string to control relay ON/OFF. Such as :
“http://192.168.1.195/1/on” for Relay1 ON
“http://192.168.1.195/1/off” for Relay1 OFF
“http://192.168.1.195/2/on” for Relay2 ON
“http://192.168.1.195/2/on” for Relay2 OFF
………..
“http://192.168.1.195/32/on” for Relay32 ON
“http://192.168.1.195/32/on” for Relay32 OFF
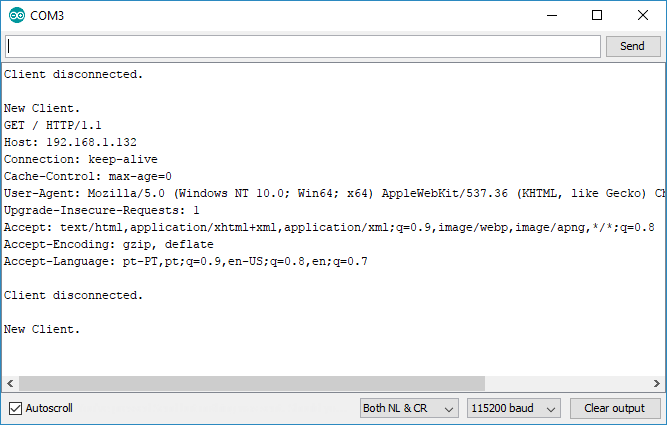
If take a look at the serial monitor, you can see what’s going on on the background. The ESP receives an HTTP request from a new client – in this case, your browser.
You can also see other information about the HTTP request – these fields are called HTTP header fields, and they define the operating parameters of an HTTP transaction.
It can also open web browser on mobile phone.